Introduction
Motivational Reflexivity is a reflective practice aimed at understanding the motivations behind our personal beliefs, especially those driven by the satisfaction of needs. Drawing from diverse theoretical foundations in psychology, sociology, and philosophy, this concept offers individuals a means to critically evaluate their beliefs and decisions. In particular, Motivational Reflexivity helps distinguish between beliefs grounded in objective reality and those formed to satisfy emotional or psychological needs. This paper explores the foundations of Motivational Reflexivity through the lenses of human needs, automaticity, reflexivity, and the morphogenic cycle, ultimately offering strategies for integrating this practice into daily life.
Needs
Human needs are fundamental conditions necessary for well-being and personal development. Drawing from theories such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (Maslow, 1943) and Alderfer’s ERG model, these encompass both basic physiological needs (e.g., food and shelter) and higher-order psychological needs (e.g., self-esteem and belonging). Needs drive our behaviour and inform our beliefs.
Satisfiers
Satisfiers are the resources or elements that fulfil or enhance the satisfaction of these needs (Max-Neef, 1991). They can be external (e.g., food, shelter, social connections) or internal (e.g., beliefs, values [9], emotional states). Not all satisfiers are grounded in reality—some might provide temporary emotional comfort without addressing the true nature of the need.
Contra-satisfiers
Contra-satisfiers are elements that reduce or threaten the satisfaction of needs. These can trigger a defensive response or reflexivity when they undermine well-being. Reflexivity often emerges in response to contra-satisfiers as individuals seek ways to address unmet needs or eliminate threats.
Emotions
Emotions act as signals and motivators in relation to needs. Positive emotions (e.g., joy, satisfaction) arise when needs are met, while negative emotions (e.g., fear, anxiety, frustration) signal unmet needs or the presence of contra-satisfiers [1]. These emotional responses often lead individuals to engage in reflexive thought, where they reassess their beliefs and behaviours to better satisfy their needs.
Consciousness
Consciousness refers to self-awareness and the ability to reflect on one’s thoughts and actions. Consciousness is underpinned by internal feedback loops, where individuals evaluate their potential actions before executing them [2]. This ability to simulate actions internally is what enables reflexivity.
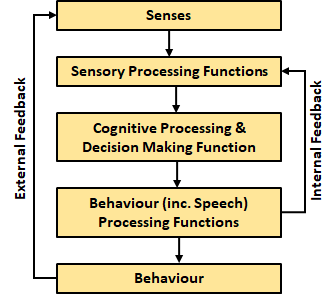
Figure 1. A simplified model of the feedback processes involved in human consciousness.
Reflexivity
Reflexivity involves engaging in internal dialogue to critically assess one’s beliefs and behaviours. It is especially important when individuals face unmet needs or threats to their well-being. Reflexivity allows for the interruption of automatic behaviour, prompting individuals to evaluate whether their beliefs align with objective reality or are motivated by personal needs.
Automaticity
Automaticity refers to habitual, unconscious behaviour that does not require reflective thought. While efficient, automaticity can prevent individuals from questioning the motivations behind their actions. Reflexivity interrupts automaticity, encouraging individuals to reexamine their decisions. For example, driving becomes an automatic task after sufficient practice, but when unexpected events occur (e.g., road hazards), reflexivity is triggered, requiring conscious engagement to adapt. [3]
The Modified Morphogenetic Cycle
The morphogenetic cycle, developed by Margaret Archer and Roy Bhaskar, describes the interaction between societal structures and individuals through a series of feedback loops (Archer, 2003)(Bhaskar, 1975). These loops shape individual beliefs and behaviours by assigning roles, norms, and expectations. When these societal roles serve as satisfiers, individuals tend to automatically affirm them. However, if societal roles act as contra-satisfiers, individuals engage in reflexivity to challenge or alter their roles and the demands made of them. [4] The modified morphogenetic cycle also includes the environment as a factor. Society’s actions impact the environment (e.g., through pollution or deforestation), which in turn affects individuals’ ability to satisfy their needs, prompting reflexivity in response to environmental degradation. [5]

Figure 2. Diagrammatic Representation of the Modified Morphogenetic Cycle.
Society (yellow circle) enculturates individuals with values [9], norms, and beliefs. Society also impacts on the natural environment (green circle) which in turn impacts on the individual. If these three impacts are satisfiers (happy person to the right) then the individual automatically affirms society. However, if one or more act as contra-satisfiers (unhappy person to the left), then the individual reflects on potential solutions and then attempts to alter society’s culture or structure accordingly. For example, he or she may alter society’s structure by leaving unsatisfactory employment.
Cultural Evolution
Cultural evolution occurs as societal norms and values [9] shift over time due to reflexivity and new ideas introduced by individuals. Reflexivity plays a central role in this evolution by allowing individuals to critically reflect on cultural elements and adopt practices that better serve their needs and goals.
Cultural Speciation
Cultural speciation refers to the emergence of distinct cultural practices from mainstream society. Reflexivity allows individuals to break away from dominant societal beliefs and form subcultures with unique values [9], norms, beliefs and structures. For example, the isolation of subcultures, such as during the Northern Ireland Troubles, led to the development of divergent cultural beliefs within a single society. [6]
Needs-Driven Beliefs
Needs-driven beliefs are those adopted primarily to satisfy personal needs, regardless of their alignment with reality. Such beliefs often arise when individuals face contra-satisfiers and adopt beliefs that provide emotional or psychological comfort (Kunda, 1990). For example, individuals might support political ideologies that align with their economic or social interests, even if the belief does not reflect broader realities. [7]
Psychological Defence Mechanisms
When needs-based beliefs are challenged, individuals may employ psychological defence mechanisms (e.g., denial, rationalisation) to protect themselves from emotional discomfort (Freud, S.,1920)(Freud, A., 1936). These defences prevent individuals from critically reflecting on the truth of their beliefs. Motivational Reflexivity challenges these mechanisms, helping individuals recognize when their beliefs are motivated by needs rather than objective truth. [8]
Motivational Reflexivity
Motivational Reflexivity involves regularly questioning the motivations behind one’s beliefs and actions. By asking questions like “Why do I hold this belief?” and “Is this belief serving a deeper emotional need?”, individuals become more conscious of the needs driving their decisions. Over time, this process allows individuals to align their beliefs more closely with reality.
Benefits for the Individual
The practice of Motivational Reflexivity leads to greater self-awareness, helping individuals uncover the underlying motivations behind their beliefs. By aligning beliefs with objective truth, individuals experience personal growth and a deeper understanding of their true needs. Reflexivity also fosters empathy, enhancing the ability to understand others’ beliefs and motivations.
Benefits for Society & the Environment
On a societal level, Motivational Reflexivity promotes cultural evolution by helping individuals challenge false beliefs that may be perpetuated through advertising, propaganda, or social pressure. It also supports sustainable practices, as individuals become more aware of the environmental impact of their actions and adjust their behaviours accordingly.
Challenges and Mitigation
While Motivational Reflexivity offers significant benefits, it can also present challenges, such as emotional discomfort (Festinger, 1957) or social conflict. Individuals may find it difficult to confront long-held beliefs, and societal resistance may arise when dominant beliefs are questioned. To mitigate these challenges, Motivational Reflexivity must be practiced with empathy and within supportive frameworks that encourage open dialogue and respect for diverse perspectives.
Conclusion
Motivational Reflexivity empowers individuals to engage in a deep, reflective practice that aligns their beliefs with reality and enhances personal growth. By regularly reflecting on the emotional and psychological needs behind their beliefs, individuals can develop self-awareness, cultivate empathy, and make more informed decisions.
On a broader scale, Motivational Reflexivity offers the potential for societal and environmental progress. By challenging the enculturation of false needs-based beliefs and promoting sustainable practices, Motivational Reflexivity can drive positive change for both individuals and the larger social and environmental systems they inhabit.
Notes
- We prioritize our needs based on the intensity of negative emotions that arise when a need goes unmet or is threatened.
- These potential actions can also be ones of speech. That is we review what we intend to say before we say it in order to judge its likely effects. The feedback loops can also be external. That is, we observe the consequences of our actions and learn from them.
- Automaticity may also arise from socialization—for example, learning cultural norms or professional routines through repeated exposure. Lastly, automaticity can be an instinctive reaction to immediate danger, such as the fight-or-flight response, which is activated without conscious deliberation to ensure survival.
- The modified morphogenetic cycle is continuously ongoing. It distinguishes between society’s cultural elements, i.e., values, norms and beliefs, and society’s structure, i.e., individual roles. Either can act as a satisfier and be automatically accepted or as a contra-satisfier triggering reflexivity and attempts to alter the situation.
- The natural environment can also produce satisfiers and contra-satisfiers independent of society, such as natural disasters (e.g., volcanoes, droughts), which impact individuals’ needs. In the early development of humanity, the natural environment played the leading role in cultural evolution but with population growth social forces now play the leading role.
- When a subculture isolates itself (geographically or ideologically), a new culture may evolve that is distinct from the original. However, if the subculture cannot isolate itself, it may be reabsorbed, modifying the dominant culture. Alternatively, if there is conflict between the cultures, it may result in tensions, such as those seen in the Northern Ireland Troubles.
- In the natural environment, needs-driven beliefs are rare, as natural phenomena (like climate) are not influenced by human beliefs. However, in social contexts, needs-driven beliefs are more common, as society can be influenced or shaped by these beliefs to satisfy personal needs.
- Psychological defence mechanisms can also be triggered when we are unable to satisfy a need or are unable to avoid a contra-satisfier.
- Values are a special type of belief, i.e., beliefs about what is good or bad. Good and bad are, in turn, defined by ethics. Values are shortcuts that avoid detailed ethical analysis. If followed in relevant circumstances they will normally lead to ethical behaviour. Furthermore, they can be propagated through society without the need for reference to the detailed ethics that underpin them. Finally, like any other belief, they can be needs-driven. So, not all people have pro-social or pro-environmental values. This of course implies that Motivational Reflexivity promotes two core beliefs. Firstly, that it is good for our beliefs to conform to reality and, secondly, that our values should be pro-social and pro-environmental.
References
- Archer, M. S. (2003). Structure, Agency and the Internal Conversation. Cambridge University Press.
- Bhaskar, R. (1975). A Realist Theory of Science. Leeds: Leeds Books.
- Festinger, L. (1957). A Theory of Cognitive Dissonance. Stanford University Press.
- Freud, A. (1936). The Ego and the Mechanisms of Defence. London: Hogarth Press and the Institute of Psychoanalysis.
- Freud, S. (1920). Beyond the Pleasure Principle. London: International Psycho-Analytical Press.
- Kunda, Z. (1990). The case for motivated reasoning. Psychological Bulletin, 108(3), 480–498.
- Maslow, A. H. (1943). A Theory of Human Motivation. Psychological Review, 50(4), 370–396.
- Max-Neef, M. A. (1991). Human Scale Development: Conception, Application and Further Reflections. New York: Apex Press.
One reply on “An Introduction to Motivational Reflexivity”
i u/stand motivational reflexibility and i think it is very useful, i wonder how many people are aware of this mental tool ????????? let alone practice it, the rest of the paper need further study
how you have acquired all this i and presumably u/stand these extremely abstract ideas i cannot grasp
janos korn
LikeLike